Face Recognition using K-Nearest Neighbors
Packages Used:-
- Python 2.7
- Numpy, SciPy
- Mathplotlib
- OpenCV Python
The K-Nearest Neighbours(Supervised Learning) Algorithm Code
record_faces.py
```python import numpy as np import cv2
instantiate a camera object to capture images
cam = cv2.VideoCapture(1)
create a haar-cascade object for face detection
face_cas = cv2.CascadeClassifier(‘./haarcascade_frontalface_default.xml’)
create a placeholder for storing the data
data = [] ix = 0 # current frame number
while True: # retrieve the ret (boolean) and frame from camera ret, frame = cam.read()
# if the camera is working fine, we proceed to extract the face
if ret == True:
# convert the current frame to grayscale
gray = cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
# apply the haar cascade to detect faces in the current frame
# the other parameters 1.3 and 5 are fine tuning parameters
# for the haar cascade object
faces = face_cas.detectMultiScale(gray, 1.3, 5)
# for each face object we get, we have
# the corner coords (x, y)
# and the width and height of the face
for (x, y, w, h) in faces:
# get the face component from the image frame
face_component = frame[y:y+h, x:x+w, :]
# resize the face image to 50X50X3
fc = cv2.resize(face_component, (50, 50))
# store the face data after every 10 frames
# only if the number of entries is less than 20
if ix%10 == 0 and len(data) < 20:
data.append(fc)
# for visualization, draw a rectangle around the face
# in the image
cv2.rectangle(frame, (x, y), (x+w, y+h), (0, 255, 0), 2)
ix += 1 # increment the current frame number
cv2.imshow('frame', frame) # display the frame
# if the user presses the escape key (ID: 27)
# or the number of images hits 20, we stop
# recording.
if cv2.waitKey(1) == 27 or len(data) >= 20:
break
else:
# if the camera is not working, print "error"
print "error"
now we destroy the windows we have created
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
convert the data to a numpy format
data = np.asarray(data)
print the shape as a sanity-check
print data.shape
save the data as a numpy matrix in an encoded format
np.save(‘face_03’, data)
We’ll run the script for different people and store
the data into multiple files
### FaceRec.py
```python
import numpy as np
import cv2
# instantiate the camera object and haar cascade
cam = cv2.VideoCapture(1)
face_cas = cv2.CascadeClassifier('./haarcascade_frontalface_default.xml')
# declare the type of font to be used on output window
font = cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX
# load the data from the numpy matrices and convert to linear vectors
f_01 = np.load('face_01.npy').reshape((20, 50*50*3)) # Shubham
f_02 = np.load('face_02.npy').reshape((20, 50*50*3)) # Prateek
f_03 = np.load('face_03.npy').reshape((20, 50*50*3)) # Laksh
print f_01.shape, f_02.shape, f_03.shape
# create a look-up dictionary
names = {
0: 'Shubham',
1: 'Prateek',
2: 'Laksh',
}
# create a matrix to store the labels
labels = np.zeros((60, 1))
labels[:20, :] = 0.0 # first 20 for shubham (0)
labels[20:40, :] = 1.0 # next 20 for prateek (1)
labels[40:, :] = 2.0 # last 20 for laksh (2)
# combine all info into one data array
data = np.concatenate([f_01, f_02, f_03]) # (60, 7500)
print data.shape, labels.shape # (60, 1)
# the distance and knn functions we defined earlier
def distance(x1, x2):
return np.sqrt(((x1-x2)**2).sum())
def knn(x, train, targets, k=5):
m = train.shape[0]
dist = []
for ix in range(m):
# compute distance from each point and store in dist
dist.append(distance(x, train[ix]))
dist = np.asarray(dist)
indx = np.argsort(dist)
sorted_labels = labels[indx][:k]
counts = np.unique(sorted_labels, return_counts=True)
return counts[0][np.argmax(counts[1])]
while True:
# get each frame
ret, frame = cam.read()
if ret == True:
# convert to grayscale and get faces
gray = cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
faces = face_cas.detectMultiScale(gray, 1.3, 5)
# for each face
for (x, y, w, h) in faces:
face_component = frame[y:y+h, x:x+w, :]
fc = cv2.resize(face_component, (50, 50))
# after processing the image and rescaling
# convert to linear vector using .flatten()
# and pass to knn function along with all the data
lab = knn(fc.flatten(), data, labels)
# convert this label to int and get the corresponding name
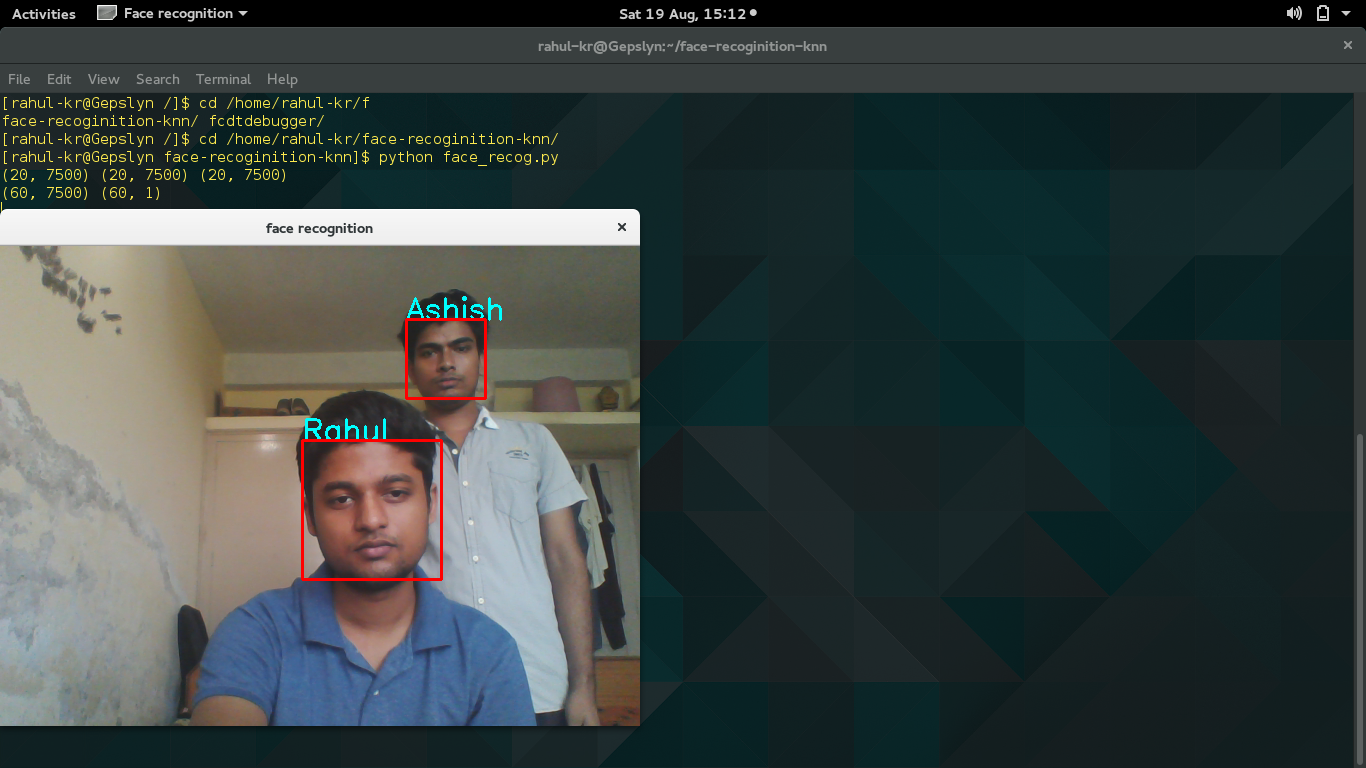
text = names[int(lab)]
# display the name
cv2.putText(frame, text, (x, y), font, 1, (255, 255, 0), 2)
# draw a rectangle over the face
cv2.rectangle(frame, (x, y), (x+w, y+h), (0, 0, 255), 2)
cv2.imshow('face recognition', frame)
if cv2.waitKey(1) == 27:
break
else:
print 'Error'
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
Project Details
Date: Aug 15, 2017
Author: Rahul Kumar
Categories: project
Tagged: Machine Learning






 Platform © Web-Development
Platform © Web-Development